The Effect of Impurities on Nickel Content In Ore Samples Using Oven and Roasted Preparation Methods
Main Article Content
Abstract
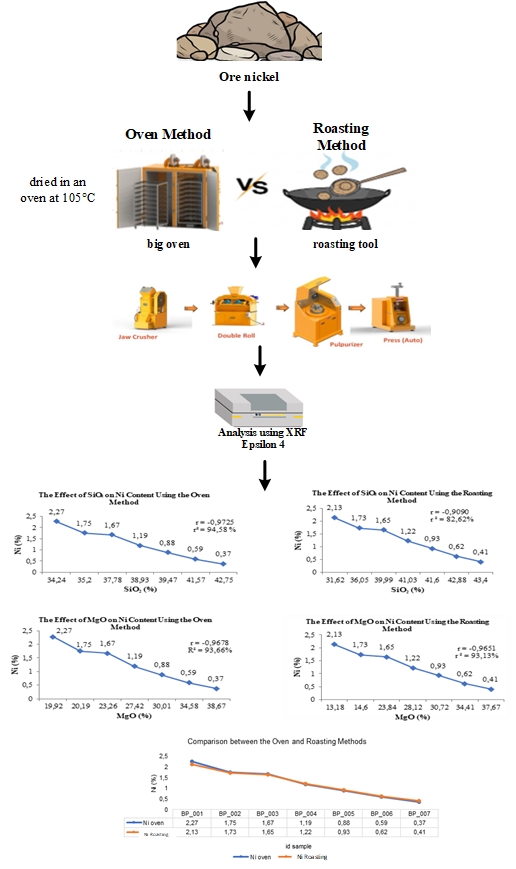
This research was conducted using two sample drying methods: the oven method and the roasting method. Elemental analysis was carried out using the X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) Epsilon 4 instrument. The study investigated the influence of impurity metals on nickel (Ni) content, particularly the presence of silica (SiO₂) and magnesium oxide (MgO). The results showed that silica (SiO₂) plays a significant role in affecting nickel content. The higher the silica content, the lower the detected nickel content. This is supported by negative correlation coefficients of -0.9725 for the oven method and -0.9090 for the roasting method. The coefficients of determination were 94.58% and 82.62%, respectively, indicating a strong relationship between silica and nickel content. In addition, the relationship between MgO and Ni also showed a negative trend. An increase in MgO content was followed by a decrease in Ni content. The correlation coefficients were -0.9678 for the oven method and -0.9651 for the roasting method, with coefficients of determination of 93.66% and 93.13%. These results confirm a very strong influence of MgO on Ni content. A t-test was conducted to determine whether there was a significant difference between the two drying methods in nickel content measurement. The calculated t-value was 0.013, while the critical t-value was 2.18. Since the calculated value is lower, the null hypothesis (H₀) is accepted, indicating no significant difference between the oven and roasting methods
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.