Effect of Fermentation Duration on the Carbon-to-Nitrogen (C/N) Ratio of Liquid Organic Fertilizer Produced from Dami Jackfruit Waste Using Coconut Husk-Based Bioactivator
Main Article Content
Abstract
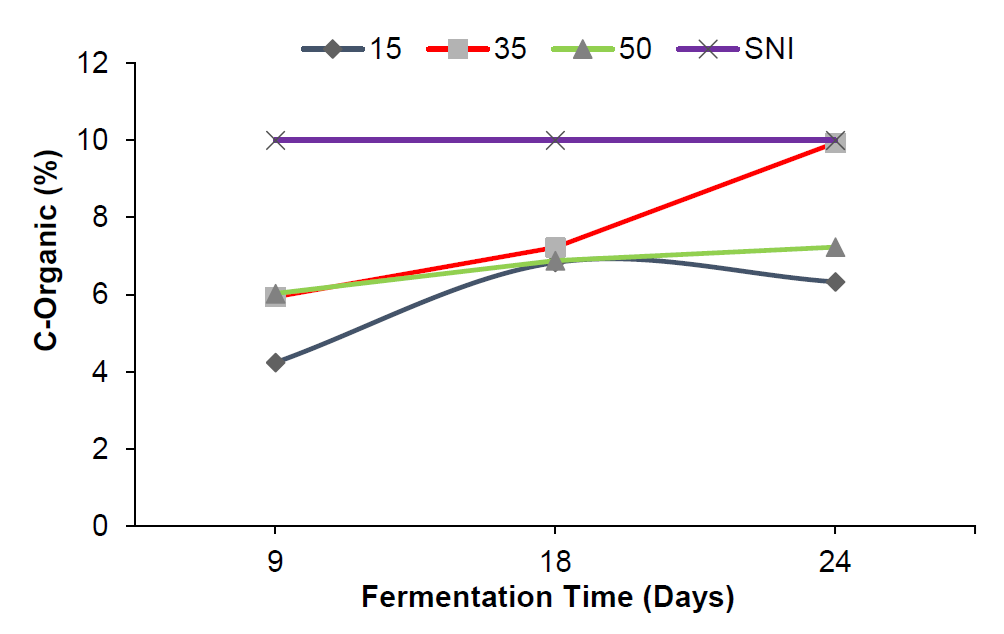
Market and household waste are significant contributors to urban pollution, leading to health issues and a decline in city aesthetics. One of the most commonly found market wastes is jackfruit dami waste. This study aims to evaluate the effect of bioactivator addition on the carbon-to-nitrogen (C/N) ratio and to determine the optimal composting duration for achieving a favorable C/N value. The bioactivator (MOL) was prepared using 300 g of coconut fiber and 5 L of coconut water, fermented for two weeks with stirring every three days to release gas. Molasses was prepared by dissolving 1 kg of granulated sugar in 1000 mL of distilled water (1:1 ratio). The jackfruit dami waste was shredded, weighed, and mixed with distilled water, molasses, and MOL at varying concentrations (5%, 11%, and 17% v/w). The composting process was carried out in sealed plastic containers for 9 to 24 days, with stirring every three days. The composted materials were then analyzed for organic carbon and nitrogen content to determine the C/N ratio. The results showed that the highest C/N ratio of 7.18% was obtained on day 24 with a 11% MOL concentration. However, based on the standards set by the Ministry of Agriculture for liquid organic fertilizers, the C/N ratio obtained in this study did not meet the required specifications.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.