Synthesis and Characterization of Composite Emulsifier from Periwinkle Shell and Gum Arabic applied in Oil-Water Emulsification Process
Main Article Content
Abstract
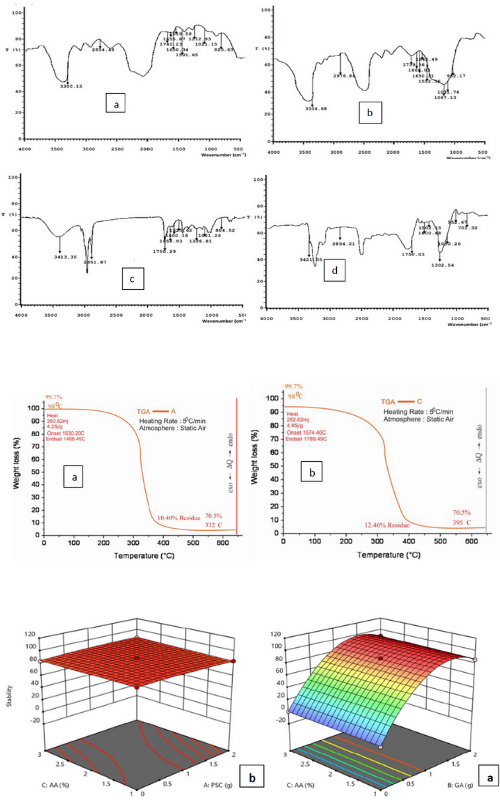
The Synthetic surfactants employed in the management of oil-polluted water through the emulsification process usually lead to introducing secondary pollutants with more toxic effects on the environment. However, the need to safely mitigate the environmental impact of oil pollution has led to the increasing demand for eco-friendly, bio-based materials for the treatment of oil-polluted water. The effect of Periwinkle Chitosan-Gum Arabic (PSC-GA) composite emulsifier on the stability of oil-water emulsion (10% v/v) was investigated. Chitosan was extracted from the Periwinkle shell through the sequential order of decolorization, demineralization, deproteinization, and deacetylation with 40% NaOH (DCMPA) resulting in a yield of 5.96%. The emulsifier was formed with mixtures of chitosan and gum Arabic at 0%, 1%, and 2% each dissolved in 1%, 2%, and 3% aqueous acetic acid (AA) solution in a randomized experimental design using Box Behnken Design (BBD) under Response Surface Methodology (RSM) of Design Expert (Version 13). An optimum composition of 1.10% PSC, 1.54% GA, and 1.51% AA for the emulsifier with 97.6% stability was obtained from the optimization of the emulsion stability index. This study shows that PSC-GA composite is an effective emulsifier capable of producing stable emulsion with CMC of 0.02 g/l at 0.039 N/m and Zeta potential of over -36 mV which could be applied for the emulsification process in the oil-polluted environment to prevent oil migration.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.